**This is a post “in-progress.” New formulas will be added, when possible, until it is completed.
Dividends are a simple concept. However, there are a lot of questions regarding their calculation.
This post attempts to answer most of those questions. If you’re wondering “how to calculate dividend _?”, the answer is probably here.
These answers are pretty straightforward, so little or no explanation is provided. Make sure you know your mathematics order of operations.
The different facets of dividend calculation are listed in alphabetical order.
Keep in mind that the same dividend calculation can have several different names.
The dividend amount you see when looking at a stock quote.
Example:
$.22 dividend per share
4 payments (quarterly)
= $.22 × 4
= $.88
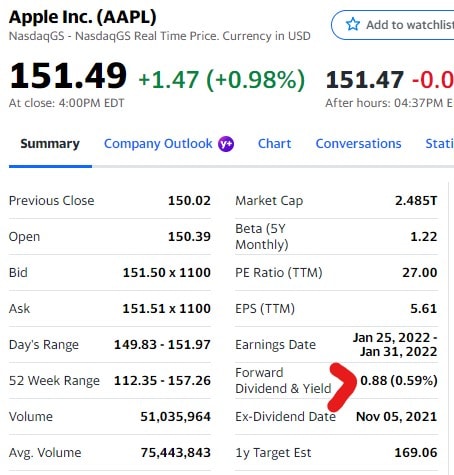
Amount from dividend yield, Amount based on yield
Use the dividend yield to calculate the annual dividend per share
Example:
0.59% dividend yield
$149.83 current stock price
= .0059 × 149.83
= $.88
Keep in mind that dividend yields aren’t as up-to-date as share prices.
After tax
How much of your dividends you get to keep after taxes.
Example (dollars):
$.88 dividend amount
15% marginal tax rate
= .88 × (1 – .15)
= $.748
Example (yield):
.59% dividend yield
15% marginal tax rate
= .0059 × (1 – .15)
= .5015%
APY
The annualized yield realized after receiving dividends over a period of time.
Example:
$7.76 dividends received
$75.55 stock purchase price
773 days held (2 years, 43 days)
= (1 + (7.76 ÷ 75.55)) ^ (365 ÷ 773) – 1
= (1.10271 ^ .47219) – 1
= .0472, or 4.7%
Annual income, Benefits
Amount of dollars in dividend income you received/can expect over the course of a year.
Example:
$.88 annual dividends per share
1,000 shares
= .88 × 1,000
= $880
Basis for reinvestment, Cost basis for dividend reivestment plan
The price at which dividends are reinvested via a DRIP.
Example:
$17.53 total dividend amount
.917 number of shares purchased
= 17.53 ÷ .917
= $19.1182
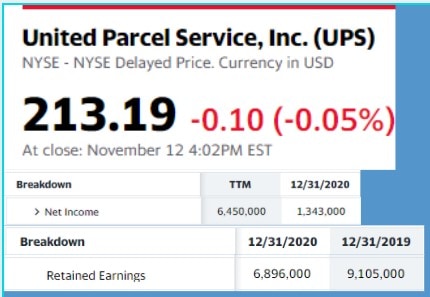
From balance sheet, Yield from balance sheet, Cash flow, Declared, Paid
Using the balance sheet and income statement to determine the total amount of dividends paid to shareholders.
Example (dollars):
$1,343,000 this years’ net profit
$9,105,000 last years’ retained earnings
$6,896,000 this years’ retained earnings
= 1,343,000 + 9,105,000 – 6,896,000
= $3,552,000
Example (yield):
$3,552,000 dividend from balance sheet
871,000 shares outstanding
$213.19 share price
= 3,552,000 ÷ 871,000
= $4.08
= 4.08 ÷ 213.19
= 1.9%
Cover, Coverage ratio
The number of times a company could (theoretically) pay dividends to common stockholders with current earnings.
Example:
$7.36 earnings per share
$4.08 dividend per share
= 7.36 ÷ 4.08
= 1.80
Compound
The contribution of dividends received from shares purchased via reinvestment.
Example:
$4.08 dividend amount
2.105 shares purchased via DRIP
= 4.08 × 2.105
= $8.59
CAGR
The annualized growth rate of a dividend.
Example:
$4.08 current dividend
$3.64 beginning dividend amount
3 years the stock has been owned
= ((4.08 ÷ 3.64) ^ (1 ÷ 3)) – 1
= .039 (3.9%)
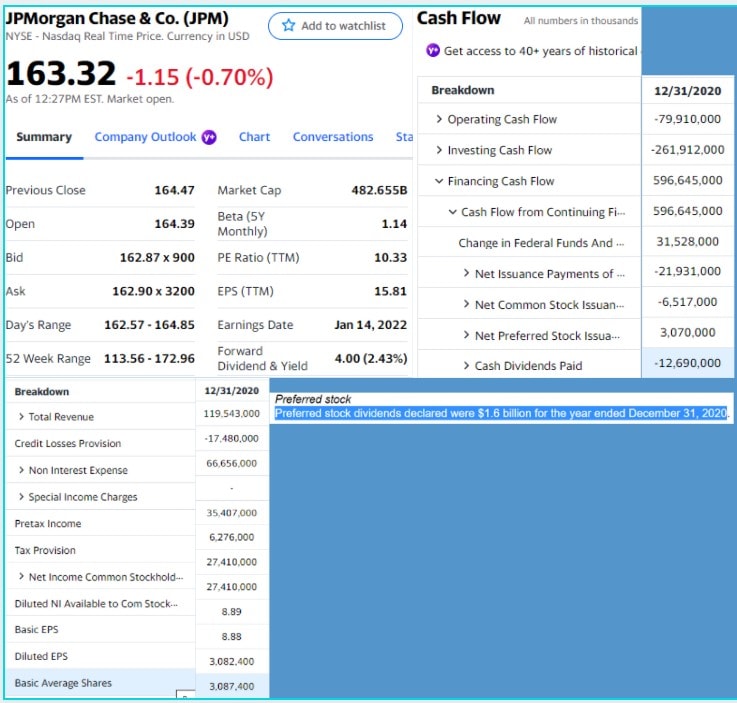
Per-share cash dividends paid by a company to common stockholders.
Example:
$12,690 total cash dividends
$1,600 preferred dividends
3,087.4 shares outstanding
= (12,690 – 1,600) ÷ 3,087.4
= $3.59
Discount model
Performing stock valuation using the present value of all future dividends.
Example:
$4.28 expected dividend
7% equity cost of capital
5% expected dividend growth rate
= 4.28 ÷ (.07 – .05)
= $214.00
DRIP
The additional return received due to reinvestment of dividends. Investment value depends on shares purchased, dividends paid, stock price appreciation, dividend growth, and time held.
Example:
$27,000 investment value with dividend reinvestment
$23,000 investment value without reinvestment
= 27,000 – 23,000
= $4,000 (+17.4%)
Contents
- Amount, Amount per share, Forward, Annualized, Annual, Annual dividend per share
- Amount from dividend yield, Amount based on yield
- After tax
- APY
- Annual income, Benefits
- Basis for reinvestment, Cost basis for dividend reivestment plan
- From balance sheet, Yield from balance sheet, Cash flow, Declared, Paid
- Cover, Coverage ratio
- Compound
- CAGR
- Cash per share, dividends per share (common)
- Discount model
- DRIP













